Alternative Medicine a public where traditional drug has long been the foundation of healthcare, volition specifics are gaining fashionability as individualities seek holistic and reciprocal approaches to heartiness. This composition aims to claw into the realm of volition specifics, interrogating their origins, principles, and notable exemplifications. From herbal remedies to acupuncture and beyond, this comprehensive companion sheds light on the different geography of indispensable drug.
I. Origins and Principles of Alternative Medications:
A. Historical Context:
Alternative medicine has deep roots in various cultures, with practices dating back centuries. Ancient civilizations such as the Chinese, Ayurvedic in India, and Native American tribes relied on natural remedies to treat ailments. alternative medicine conventions laid the institution for the holistic principles that characterize numerous volition specifics moment.
B. Holistic Approach:
One key principle of alternative medications is the holistic approach to health. Unlike conventional medicine, which often focuses on treating specific symptoms or diseases, alternative medicine considers the interconnectedness of the mind, body, and spirit.This passage aims to promote overall well- being by addressing the root causes of fitness issues.
II. Types of Alternative Medications:
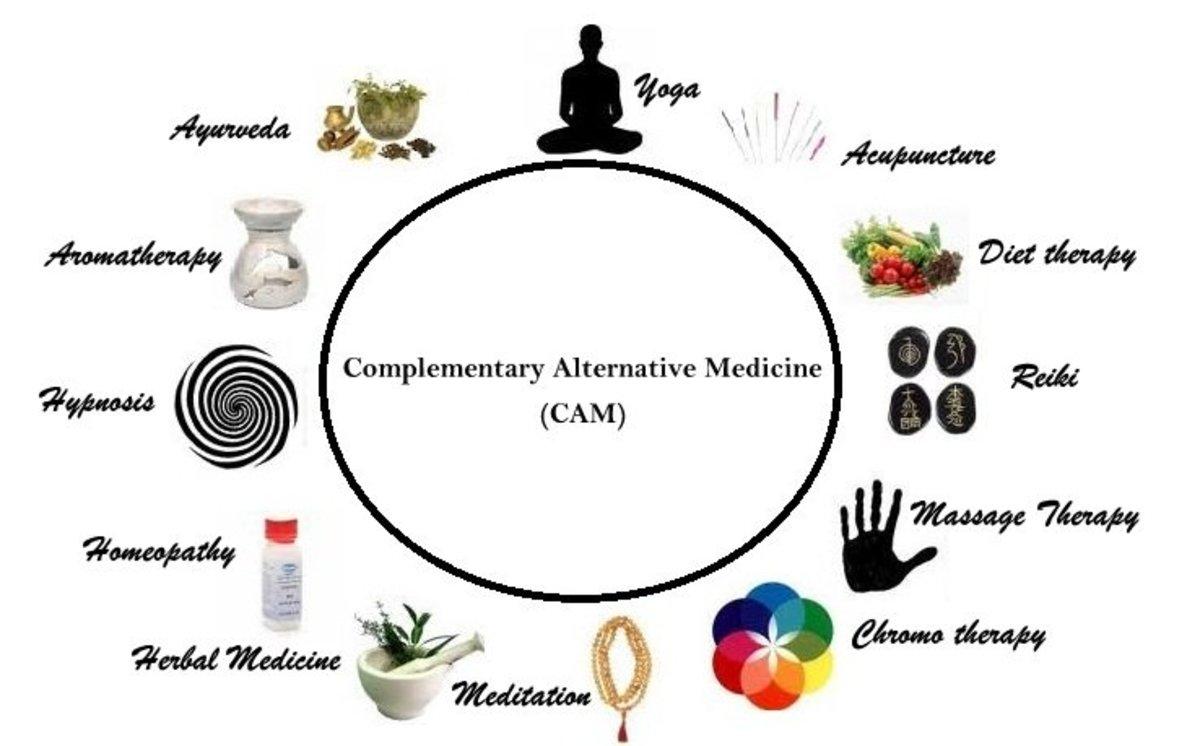
chosen drug encompasses a different range of practices, curatives, and products that aren’t considered customary or mainstream drug. It’s important to note that while some indispensable curatives may have probative substantiation, others may warrant scientific backing.Always consult with a healthcare professional before trying any alternative treatment. Here are some types of alternative medications:
Herbal Medicine:
Uses plants and plant extracts for medicinal purposes. Exemplifications contain echinacea for vulnerable mount, chamomile for relaxation, and ginseng for energy.
Acupuncture:
Originating from traditional Chinese medicine, acupuncture involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate energy flow and promote healing.
Ayurveda:
An ancient system of medicine from India that focuses on balancing the body’s energies (doshas) through diet, herbal remedies, and lifestyle practices.
Homeopathy:
Based on the principle of “like cures like,” homeopathic remedies use highly diluted substances to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes.
Chiropractic Care:
Involves the manipulation of the spine to treat musculoskeletal conditions, with the belief that proper alignment promotes overall health.
Naturopathy:
Emphasizes the body’s ability to heal itself using natural therapies such as herbal medicine, nutrition, and lifestyle changes.
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM):
Includes various practices like acupuncture, herbal medicine, cupping, and tai chi, with the goal of balancing the body’s vital energy (qi).
Aromatherapy:
Involves the use of essential oils extracted from plants to promote physical and psychological well-being through inhalation or topical application.
Mind- Body Interventions dry runs that concentrate on the bearing between the mind and body, similar as contemplation, yoga, and biofeedback.
Energy Healing:
Encompasses modalities like Reiki, therapeutic touch, and qigong, which aim to balance the body’s energy fields for healing.
Functional Medicine:
Focuses on addressing the root causes of illness through a holistic approach, considering factors such as lifestyle, genetics, and environment.
Traditional African Medicine:
Diverse healing practices rooted in various African cultures, often involving the use of herbs, rituals, and spiritual elements.
It’s critical to approach indispensable drug with an open mind but also a critical perspective. While some practices have demonstrated efficacy for certain conditions, others may lack scientific validation or could interact with conventional treatments. Always consult with healthcare professionals, and inform them of any alternative treatments you’re considering.
A. Herbal Remedies:
Overview:
Herbal remedies involve the use of plants and plant extracts to prevent or treat various ailments. This dry run is deeply embedded in traditional drug and continues to be a significant element of indispensable healthcare.
Examples:
Echinacea: Widely used to boost the immune system. b. Turmeric: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties. c. Ginkgo Biloba: Believed to enhance cognitive function.
B. Acupuncture:
Principles:
Acupuncture, an ancient Chinese practice, involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to balance the flow of energy, or “qi.” This is believed to promote healing and alleviate pain.
Applications:
Pain Management: Acupuncture is commonly used to address chronic pain conditions. b. Stress and Anxiety: Some individuals find relief from stress and anxiety through acupuncture sessions.
C. Homeopathy:
Basics:
Homeopathy operates on the principle of “like cures like,” where highly diluted substances that would cause symptoms in a healthy person are used to treat similar symptoms in an ill person.
Controversies:
While some individuals swear by homeopathic remedies, Alternative Medicine scientific community often questions the efficacy of highly diluted substances.
III. Integration with Conventional Medicine:
-
Complementary vs. Alternative Medicine:
Complementary Medicine: Used alongside conventional treatments to enhance their effects.
Alternative Medicine: Used in place of conventional treatments.
B. Holistic Healthcare:
An increasing number of healthcare providers are adopting a holistic approach that combines both conventional and alternative treatments to provide more comprehensive care. This integrative model aims to leverage the strengths of both approaches.
IV. Research and Evidence:
A. Scientific Scrutiny:
While alternative medications have gained popularity, their efficacy is often a subject of debate within the scientific community. Some remedies have been extensively studied and proven effective, while others lack robust scientific evidence.
B. The Placebo Effect:
The placebo effect plays a significant role in the perceived effectiveness of many alternative medications. Understanding the psychological and physiological impact of belief on healing is crucial in evaluating these treatments.
V. Popular Trends and Emerging Therapies:
A. Mind-Body Practices:
Meditation and Mindfulness: Growing in popularity for stress reduction and mental well-being.
Yoga: Blending physical postures, breath control, and meditation for holistic health.
B. Cannabidiol (CBD):
The rise of CBD products has sparked interest in the potential therapeutic benefits of cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. From pain management to anxiety relief, CBD is being explored for various health applications.
VI. Safety and Regulation:
A. Quality Control:
One challenge in the alternative medicine landscape is ensuring the quality and safety of products. Lack of regulation can lead to variations in product potency and purity.
B. Consultation with Healthcare Professionals:
Individuals considering alternative medications should consult with healthcare professionals to ensure compatibility with existing treatments and to receive guidance on safety and efficacy.
Conclusion:
As alternative medications continue to gain recognition, it’s crucial to approach them with an informed and balanced perspective. While some practices have withstood the test of time and scientific scrutiny, others may lack robust evidence. A collaborative approach that integrates the strengths of both conventional and alternative medicine holds promise for a more comprehensive and personalized healthcare system. In the ever-evolving landscape of health and wellness, understanding the principles, types, and potential benefits of alternative medications contributes to a more informed and empowered approach to individual well-being.